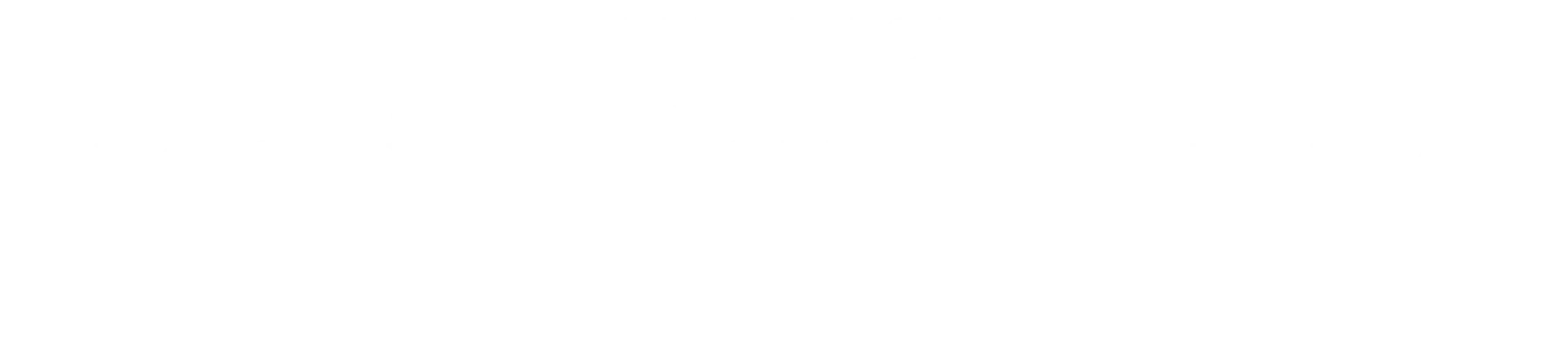Adult & Adolescent
Brachial Plexus Injuries
What is Brachial Plexus Injuries?
Complete Brachial Plexus Injuries
These are the most severe and involve injury to all of the nerves. The degree of injury tends to also be very high which means that very few, if any, components of the nerve remain in continuity. Surgery is critical for these patients. While the options for surgery are less than in partial injuries, there remains much that can be done to improve the function of the patient.
Partial Brachial Plexus Injuries
These are the most common type but also a very heterogeneous group. Some of these injuries are very mild and will recover on their own with an essentially normal outcome. Other partial brachial plexus injuries can be much more severe and are comparable to complete brachial plexus injuries. It is critical to be evaluated by an experienced team of physicians to determine the number of nerves affected and the degree to which they are affected.
Categories of Brachial Plexus Injuries
When your arm, hand or fingers awkwardly, or lacks strength or reflexes, or you can visually detect deformation of your baby’s arm and/or hand, you ought to have your baby tested for Brachial Plexus injuries.
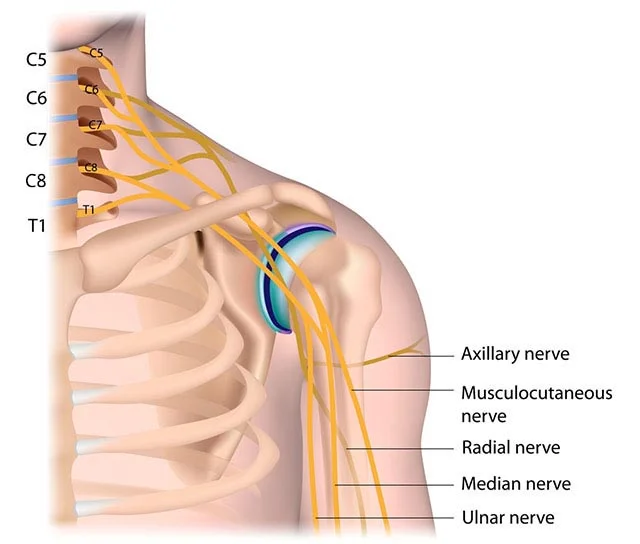
What is the role of therapy?
The Key Role Therapeutic Interventions Play in Early Stages
The importance of therapy cannot be stressed enough as some patients were able to avoid surgery with our well-designed therapeutic interventions. Our therapists help to prevent limitations in range of motion, limit muscle atrophy, and use technology to support recovery.
If surgery is required, our therapy team is equipped to manage all your post-operative needs. Therapists will work with you to determine how often you need to be seen in the clinic, continue to update your home program, and help you return to the activities you enjoy.
Full Spectrum of Advanced Therapeutic InterventionAdvanced technologies and innovative treatments are available to adolescents and adults with Brachial Plexus injuries at the Center for Brachial Plexus Injuries at NYU Langone Health.
The most advanced therapy intervention program in the nation
Our comprehensive evaluation includes:
- Assessment of function
- Collaborative goal setting
- Use of interpreter services
- Support services
- Telehealth
The most advanced therapy intervention program in the nation! We use the most effective treatment techniques that are individualized to your needs. Our therapy treatments include:
- Individualized Stretching/Strengthening Program
- Custom Splinting
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
- Therapeutic Taping
- Serial Casting
- Modified Constraint Induced Movement Therapy
- Aquatic Therapy
- Robotic & Virtual Technology
- In-home therapy in Manhattan, Westchester and Connecticut
No Brachial Plexus injuries are the same
Surgical Treatment
There exist many different types of surgical options for patients. Seeing that Brachial Plexus Injuries are by definition nerve injuries, surgery of the nerves are very common. There is a window of time where nerve surgery is a possibility. This time period is determined by how long muscle can remain denervated before it becomes too late to successfully reinnervate the muscle and allow for meaningful function. This period of time is commonly said to be 18 months.
If the patient presents early enough, they may be a candidate for Brachial Plexus Reconstructive Surgery. This is a microsurgical nerve approach that either treats or replaces damaged nerves to reduce pain, or restores sensation and motor movements in the arm. How we determine whether you need surgery or not, what type of surgery(s), and the sequence of surgeries (if multiple are needed) depend on several key factors such as the timing and severity of the nerve injury sustained, but also the overall health, activity and age of the patient.
Are there other possible treatments for BPI?
There is much about nerve injury and nerve healing that is very poorly understood. Despite that, non-surgical treatment options for BPI like stem-cell therapy do exist. However, these have very little to no support in medical literature. Anecdotally, we have seen several patients who have undergone treatment options that are not standard of care. Many of these patients have reported significant and tangible improvements in their function. The medical explanation for this remains evasive. We do not encourage pursuing other non-surgical treatment options. But we also do not actively discourage the pursuit of other treatment options as long as 1) there is strong evidence for its safety and 2) that the cost of treatment is not prohibitive by putting the patient or the patient’s family in financial distress.
Shoulder Treament
The shoulder joint has the most motion of any joint in the body and elevation of the shoulder is a complex motion involving a coordinated combination of two joints.
Elbow Treatment
In many patients with Erb’s palsy, a mild paradoxical elbow flexion contracture often develops. To date, there is no definitive explanation of when and why this occurs.
Patient Story
This patient (who wished to be anonymous) injured his brachial plexus when he had a motorcycle accident. This video was recorded during his primary assessment as a part of primary Brachial Plexus exploration.
In his case, we determined that reconstructive surgery was necessary to regain some of the mobility, sensory and strength in his injured arm. His treatment plan included: Nerve grafting, trapezius muscle transfer and occupational therapy.
In this post-surgery video, his injured arm shows some improvements in strength. At this point, he has had extensive occupational therapy sessions for several months. His inadequate muscle functions were corrected by the surgery. His arm regained more control and stability as well.
What is Brachial Plexus Reconstructive Surgery
How do we determine whether you need surgery or not
Depending on the severity of the injury sustained, different types of individualized treatments are offered. Brachial Plexus reconstructive surgery is necessary when therapeutic intervention and neurological recovery falters, shoulder subluxation or dislocation occurs, or contracture becomes fixed.
Recovery
The recovery of function from brachial plexus injury is different for every patient. Recovery of function depends on the magnitude of the injury in terms of the number of nerves involved, the severity of the injury to each nerve and the mechanism of the trauma. The treatment selected is specific for each patient taking into account all of these factors. If surgery is required to optimize function, the surgical plan is tailored to each patient and the specific injury to the nerves of the brachial plexus. A general rule is that full recovery may take up to 2 years. Of course, every patient and condition are different. But the summary is that it will take a long time.
“These injuries are very complex and patients require a thoughtful and sophisticated plan for their treatment.”
Dr. Jacques H. Hacquebord
Make an appointment with us
(An in-house or a video visit)
212-598-2391
Monday Through Friday
9:00AM to 5:00PM (except holidays)
Ask us about your Brachial Plexus
Condition
We are here to help you plan you Brachial Plexus treatments
Share your Brachial Plexus story
with the community
Your story can inspire or help others
with Brachial Plexus injury.